IS CLIMATE CHANGE MAN-MADE?
The text of the seminar I presented at Mae Fah Luang University in Thailand in 2009.
Some parts I have updated.
The Earth's upper atmosphere receives in average 174 petawatts (1.74 ×1017 W) of incoming solar radiation[1]. A part of it is reflected, so Earth surface gets 1.2 ×1017 W.
The total worldwide energy, used by humans (oil, coal, gas, nuclear, and renewable) supply is 1.504×1013 W [2]. That says that the rapport
is ~1/8 000. Our participation in Earth's energy balance is very small. We are too weak for the competition with the Sun.
Fig. 1 represents the Earth's surface temperature anomaly measured by terrestrial climate stations as a function of time. [1]
Zero anomaly (blue line) represents the average temperature. The temperatures close to average temperature have been from1940 to 1980. From 1880 to 1940 the Earth temperature has been cooler and from 1980 to 2018 has been hotter than average.

Fig.1a Earth temperature measured from the space (NASA).
NASA states: “Unlike the surface-based temperatures,
global temperature measurements of the Earth's lower atmosphere obtained from satellites reveal no definitive warming trend over the past two decades. The slight trend that is in the data actually is mild cooling. The largest fluctuations in the satellite temperature data are not from any man-made activity but from the natural phenomena such as large volcanic eruptions from Mt. Pinatubo, and from El Niño. So, the programs which model global warming in a computer say the temperature of the Earth's lower atmosphere should be going up markedly, but actual measurements of the temperature of the lower atmosphere reveal no such pronounced activity."
Global warming scientists claim that the GW is due to the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the Earth atmosphere, but there is no similarity between the curve of Earth temperature anomaly (Fig 1) and the content of carbon dioxide in the Earth atmosphere (Fig 2).
Between 1940 and 1980, there is a small change in Earth temperature (Fig.1), while carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases 6 times.
Fig. 2 Global fossil carbon emissions 1800–2007.
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_dioxide_in_Earth%27s_atmosphere#/media/File:Global_Carbon_Emissions.svg)
Terrestrial observations of temperature changes
The GW scientists claim that the Arctic ice is melting. That is true for some years and some parts of the Arctic ice. But sometimes the ice surface coverage is increasing, as it is shown in the NASA photograph. Arctic sea ice up 60 percent in 2013
NASA satellite images show the changing Arctic sea ice coverage from August 2012 (left) to August 2013 (right) -- a growth of about a million square miles. (NASA)
Ice melting may be due to other causes than GW[3]
Reliability of terrestrial measurements data on global warming
Are the data reliable? Not all of them.
Brooks investigated Historical Climate Network (USHCN) sites in Indiana and assigned 16% of the sites an ‘excellent’ rating, 59% a ‘good’ rating, 12.5% a ‘fair’ rating, and 12.5% ‘poor’ rating. (May 2007 Purdue University West Lafayette, Indiana)
The conclusion of the paper [5]: “The use of temperature data from poorly sited stations can lead to a false sense of confidence in the robustness of multi-decadal surface air temperature trend assessments”
A more serious problem is that data do not exist for all countries for all periods cited by GW scientists.
But the biggest problem with the US data is that the weather in the US is influenced by El Nino and La Nina [5].
Such an influence exists for all Northern and Southern Americas and Australia, but much less for other countries. On the other hand, other countries may have their own influences (see Golf stream).
- The energy balance of the Earth
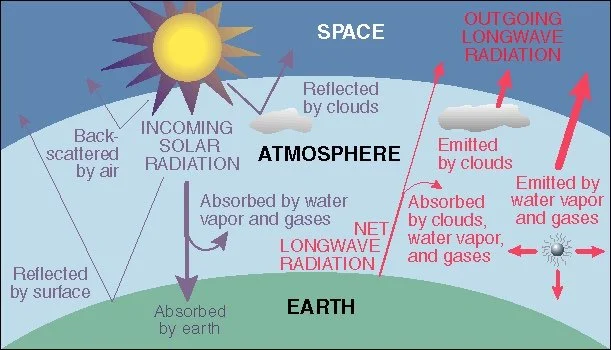
Fig 3 shows incoming and outgoing radiation
The Greenhouse effect presented in the right low corner of figure 3
Fig 4. The solar radiation spectrum shows water and CO2 absorptions bands. Water absorption bands are much stronger than that of CO2. The importance of water vapor is frequently not taken into consideration by environmental activists and by the media.
Climate change
In climate science, radiative forcing or climate forcing [6] is defined as the difference of insolation (sunlight) absorbed by the Earth and energy radiated back to space. Typically, radiative forcing is quantified at the tropopause in units of watts per square meter of the Earth's surface. A positive forcing (more incoming energy) warms the system, while negative forcing (more outgoing energy) cools it. Causes of radiative forcing include among other changes in insolation and the concentrations of radiatively active gases, commonly known as greenhouse gases and aerosols.
Fig 5. The "radiative forcing" (that is the additional energy sent to the ground) for all the modifications induced by the man that influence the energy exchanges in the atmosphere (in Watts per square meter).
The total radiative forcing is positive and equal to 2.3 +- 0.9 (W m-2)
The solar constant is the amount of incoming solar electromagnetic radiation per unit area that would be incident on a plane perpendicular to the rays has a value 1361 W/m². The total net anthropogenic (manmade) radiation forcing is 2.3 W/m² (Fig.5). The man-made radiation [2.3 (W.m-²) /1361 (W.m-²) = 0.0017 of solar constant] is very small compared to the Sun radiation.
Two important causes of the Earth temperature change are Greenhouse Gases increasing the Earth temperature and Earth Albedo lowering it.
Greenhouse effect (GHE)
Gas molecules absorb energy emitted by Sun or Earth and emit it. Part of emitted energy goes up to space, another part of energy goes down back to the Earth heating it. This effect presented in the right low corner of figure 3 is named the Greenhouse effect (GHE) [7]
GHE gases content in atmosphere:
water vapor (H2O), 0.40% over full atmosphere, typically 1%-4% at surface
carbon dioxide (CO2) 0.038%
methane (CH2) 0.000179%
nitrous oxide (N2O) 2x10−6%
ozone (O3) 0% to 7x10−6%
The distinction between the greenhouse effect and real greenhouses can be found at
Excerpt
There are papers on GHE, pro, and contra [8-9]. The discussion shows that the large temperature increases predicted by many computer models are unphysical and inconsistent with results obtained by basic measurements. Skepticism is warranted when considering computer-generated projections of global warming that cannot even predict existing observations.
Earth Albedo
Albedo is the fraction of solar energy (shortwave radiation) reflected from the Earth back into space. Earth Albedo grew after 1998 showing a cooling period. Change to the Earth's albedo is a powerful driver of climate. When the planet's reflectivity increases, more incoming sunlight is reflected back into space. This has a cooling effect on global temperatures. Conversely, a drop of albedo warms the planet.
Albedo is the fraction of solar energy (shortwave radiation) reflected from the Earth back into space. Earth Albedo grew after 1998 showing a cooling period. Change to the Earth's albedo is a powerful driver of climate. When the planet's reflectivity increases, more incoming sunlight is reflected back into space. This has a cooling effect on global temperatures. Conversely, a drop of albedo warms the planet.
Fig 6: Albedo anomalies reconstructed from ISCCP satellite data (black) and Earthshine-observed albedo anomalies (blue). The right-hand vertical scale shows negative radiative forcing (e.g. - cooling). One of the causes of the albedo rising is deforestation.
Albedo anomaly is changing strongly from one year to another (0 to 7W/sq m).
Historic climate change
Fig 7. Historic climate change (millions of years ago)

The historic climate change [11] shows that we are in a cool period and warming:
today Earth temp ~14 C
Fig 8. Historic climate change (thousands of years ago)
- 18,000 years ago - The climate begins to warm
- 15,000 years ago - Advance of glaciers halts and sea levels begin to rise
- 10,000 years ago - Ice Age megafauna goes extinct
- 8,000 years ago - Bering Strait land bridge becomes drowned, cutting of migration of men and animals.
- 6,000 years ago - The Holocene Maximum warm period
The basic processes that determine Earth climate
1. Astronomical Earth parameters
2. Oceans
3. Greenhouse Effect
4. Earth black body radiation
Astronomical Earth parameters
Astronomer Milutin Milankovitch (1879 – 1958) [13] studied the variations in the shape of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth’s axis. He theorized that these cyclical changes and the interactions among them were responsible for the long-term climate. His cycles of the climate change are roughly 100,000; 26,000 and 11,000 years.
More recent evidence of climatic variations
The eruption of the Toba supervolcano on Sumatra (Indonesia), 70,000 to 75,000 years ago reduced the average global temperature by 5 degrees Celsius for several years and may have triggered an ice age. The simulation of this event showed that the climate recovered over a few decades [14].
The eruption of the Toba supervolcano on Sumatra (Indonesia), 70,000 to 75,000 years ago reduced the average global temperature by 5 degrees Celsius for several years and may have triggered an ice age. The simulation of this event showed that the climate recovered over a few decades [14].
A much smaller but similar effect occurred after the eruption of Krakatoa in 1883 [15], island between Java and Sumatra in Indonesia when global temperatures fell for about 5 years in a row. Average global temperatures fell by as much as 1.2 degrees Celsius in the year following the eruption. Weather patterns continued to be chaotic for years and temperatures did not return to normal until 1888.
Earth has recovered after these two catastrophes.
Processes stabilizing Earth’s temperature
The basic items that stabilize the Earth climate are:
1. Water (oceans, clouds, water vapors)
2. Earth blackbody radiation
An excellent paper “Global Energy Transfer, Atmosphere and Ocean Circulation, Climate “ [16] discusses the stabilizing effect of water on climate
Excerpt: “Water has a substantially higher heat capacity than rocks (by a factor of five), and therefore the oceans can store much more heat than the land surfaces of the planet. Because the oceans also cover about 70% of the Earth surface and are on average 3.8 km deep, they are the major heatsink of the planet and serve as temperature buffers for the ocean/atmosphere system. The bulk of the thermal energy at the Earth's surface is stored in the oceans. The large thermal inertia of the oceans is a key factor in stabilizing Earth's climate.”
Earth radiation. The Stefan–Boltzmann law
This law states that the amount of thermal radiation emitted per second per unit area of the surface of a black body is directly proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature. That is
W = σ x T4
where W is the total energy radiated per unit area per unit time, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and σ = 5.67×10-8 W m-2 K-4 is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant.
If we suppose that the Earth temp T = 14 C = 287 K increases by 1C to T=15 C = 288 K, the increase in emitted energy will be 1.4%.
(W1-Wo)/Wo=1.4% is a big energetic change.
“Scientists and skeptics”
There is a site which considers that all scientists are for global warming, but in reality, some of them are skeptics [17]
There are 75 questions of skeptics and ‘science” responses to them.
I think if someone can put 75 questions to a problem, we can consider that the problem is too complex to be solved.
Global Warming Petition [18]
This petition has been signed by over 31,000 American scientists
• We urge the United States government to reject the global warming agreement that was written in Kyoto, Japan in December 1997, and any other similar proposals. The proposed limits on greenhouse gases would harm the environment, hinder the advance of science and technology, and damage the health and welfare of mankind.
There is no convincing scientific evidence that human release of carbon dioxide, methane, or other greenhouse gasses is causing or will, in the foreseeable future, cause catastrophic heating of the Earth's atmosphere and disruption of the Earth's climate. Moreover, there is substantial scientific evidence that increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide produce many beneficial effects upon the natural plant and animal environments of the Earth."
Conclusions
There are many natural influences on the Earth's climate. The influence of carbon dioxide only one of them and it is not the strongest one. However, Earth has temperature stabilizing factors by means of the water balance, the Earth radiation and others.
Global warming is most probably due to natural fluctuations, it is not Man-made. We have to study more thoroughly the climate change in order to understand its causes and effect.
The most urgent man-made problem is pollution. We can and must solve it.
References
1. What Is Solar Energy
https://www.universetoday.com/73693/what-is-solar-energy/
2. Key world energy statistics https://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/KeyWorld2017.pdf
3. Researchers discovered volcanic heat source under major Antarctic glacier
https://phys.org/news/2018-06-volcanic-source-major-antarctic-glacier.html
4. “Documentation of Uncertainties and Biases Associated with Surface Temperature Measurement Sites for Climate Change Assessment.”
5. El Niño Advisory
6. Radiative_forcing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiative_forcing
7. Greenhouse_effect
9. Top Pro & Con Arguments
10. Earth Albedo
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/earth-albedo
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/earth-albedo
11. Paleoclimatology - The Study of Ancient Climates
13. Astronomer Milutin Milankovitch (1879 – 1958)
14. Robock, A., C.M. Ammann, L. Oman, D. Shindell, S. Levis, and G. Stenchikov (2009)]. [ "Did the Toba volcanic eruption of ~74k BP produce widespread glaciation?". Journal of Geophysical Research 114: D10107
15. 1883 eruption of Krakatoa
16. Global Energy Transfer, Atmosphere and Ocean Circulation, Climate http://www.indiana.edu/~geol105/1425chap4.htm
17. Global Warming & ClimateChange Myths,
https://skepticalscience.com/argument.php
18. Global Warming Petition
© Galina Popovici, 2019 All rights reserved







